As electric vehicles (EVs) evolve, the pressure on manufacturers to ensure the performance and reliability of every sealed component continues to grow. From battery modules to sensor housings and control electronics, even microscopic leaks can have significant consequences, such as corrosion, contamination, or long-term failure.
Micro-leak testing provides the precision needed to safeguard sensitive systems and uphold quality at every stage of production.
Understanding the Risk of Micro-Leaks
EV components are exposed to intense thermal cycling, vibration, and humidity. Leak pathways invisible to the eye can allow moisture, gas, or dust to enter sealed enclosures.
Typical consequences include:
- Moisture ingress leading to internal corrosion or swelling
- Gas contamination affecting sensor accuracy or triggering faults
- Dust penetration impairing optics, MEMS, or circuit paths
- Gradual degradation impacting warranty claims and user confidence
Detecting these faults during manufacturing prevents latent field failures and supports long-term product durability.
Battery Modules: Containment and Safety
Battery modules must maintain integrity under pressure, heat, and vibration. Sealing failures may allow external moisture or air to enter, or internal gases to escape.
Leak testing protects against:
- Electrical shorts caused by vapor ingress
- Pressure instability due to trapped or escaping gases
- Compromised insulation or dielectric properties
- Thermal propagation risks in stressed cells
Accurate micro-leak detection ensures consistent containment across every module and assembly.
Sensor Systems: Sealed for Precision
Modern EVs use numerous sensors for control, monitoring, and safety. These components are often miniaturised and exposed to challenging environments.
Micro-leak testing helps confirm that sensor housings remain sealed, avoiding:
- Shift in signal accuracy due to humidity or gas exposure
- Failure in coatings or conformal seals
- Environmental interference with sensitive electronics
- Malfunction in ADAS or critical vehicle functions
Validating the seal integrity of sensors ensures consistent performance throughout the vehicle’s life.
Techniques in Micro-Leak Testing
Leak testing methods must match both the material and function of the component. For micro-level detection, commonly used techniques include:
Helium Mass Spectrometry
Detects extremely small leaks using helium as a tracer gas. Suitable for high-precision applications including battery housings and sensor modules.
Tracer Gas Sniffing
Effective for locating specific leak points in assemblies, connectors, and enclosures.
Pressure Decay and Differential Pressure
Efficient for medium-to-high throughput production environments. Offers fast, non-destructive testing for many electronic components.
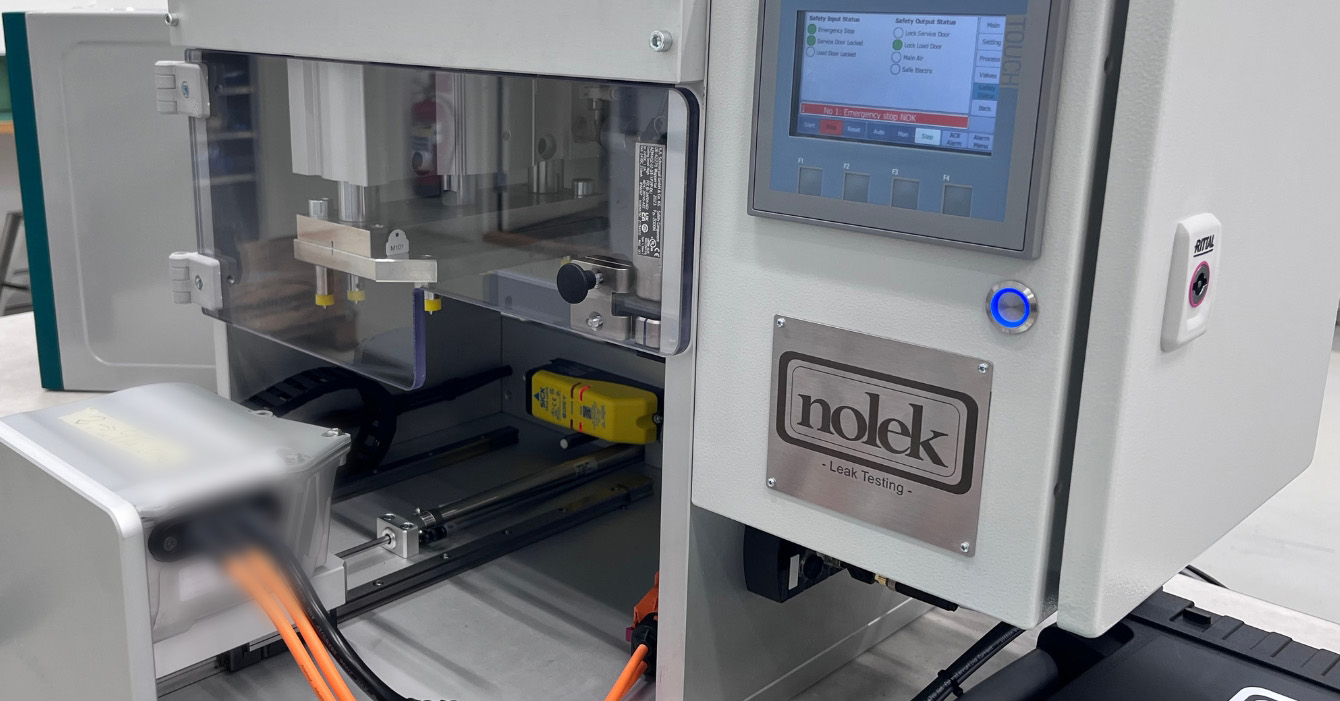
Our Approach to Leak Testing in EV Applications
We design and manufacture high-performance leak testing systems tailored for the EV and electronics industries. Our solutions cover:
- Battery modules and battery management systems
- Environmental and MEMS sensors
- Sealed electronic control units (ECUs)
- Fluid connectors and cooling assemblies
Systems are available for inline, semi-automated, and offline configurations, supporting full integration with factory MES systems and data traceability requirements.
Each solution is optimised to meet specific packaging challenges, test speeds, and sensitivity thresholds, helping manufacturers reduce scrap, improve yield, and accelerate time to market.
Wrapping Up
In EV manufacturing, the ability to detect and manage micro-leaks is central to product quality, reliability, and safety. As packaging becomes more compact and performance expectations rise, precision leak testing is a core enabler of success.
Whether you are scaling production or validating a new platform, the right micro-leak detection strategy ensures your components perform as expected, every time.
→ Learn more about Nolek’s solutions for EV and electronics